Disease and conditions
This section discusses various disease conditions. Click the read more button to continue reading the session.
Fetor hepaticus
Fetor hepaticus is a distinctive musty, sweet breath odor indicating advanced hepatic encephalopathy, a life-threatening complication of severe liver disease. Its detection requires urgent assessment of consciousness, airway, and hemodynamic status, with management focused on reducing blood ammonia and supporting vital functions.
Fecal Incontinence
Fecal incontinence is the involuntary passage of feces due to impaired anal sphincter control, resulting from gastrointestinal, neurologic, or psychological disorders, surgery, or drug effects. Its severity, pattern, and associated symptoms guide diagnosis and individualized management.
Fatigue
Fatigue is a subjective sensation of persistent tiredness, lack of energy, or exhaustion, often worsened by activity and relieved by rest. It may result from normal physical exertion, psychological stress, or underlying medical conditions such as infection, endocrine disorders, cardiovascular disease, or metabolic imbalances.
Fasciculations
Fasciculations are involuntary, visible muscle twitches caused by spontaneous motor nerve discharge, which can be benign or indicate serious neuromuscular disorders. Prompt evaluation is essential to identify underlying causes such as motor neuron disease, spinal cord lesions, or toxin exposure.
Ophthalmic Signs Reference Guide
Eye discharge, eye pain, and exophthalmos are critical ophthalmic signs that may indicate infections, trauma, inflammation, systemic disease, or vision-threatening emergencies. Accurate evaluation, timely intervention, and patient education are essential to preserve vision and ocular health.
Erythema
Erythema is a clinical manifestation of skin inflammation or irritation caused by diverse factors including infections, autoimmune disorders, drug reactions, and burns. Recognizing the underlying cause, assessing severity, and providing timely emergency interventions and supportive care are essential for effective management in healthcare settings.
Facial edema
Facial edema is swelling of the face that may be localized or generalized, developing gradually or abruptly, and can result from trauma, allergy, systemic disorders, or drug reactions. Severe cases may compromise the airway, requiring urgent intervention, while mild cases often precede peripheral or generalized edema.
Edema of the Arm
Arm edema is the accumulation of excess interstitial fluid in one or both arms, often due to trauma, vascular disorders, toxins, or treatment-related complications. Early assessment, elevation, and careful monitoring are essential to prevent complications such as neurovascular compromise and lymphedema.
Generalized Edema
Generalized edema is the widespread accumulation of interstitial fluid throughout the body, often resulting from cardiac, renal, hepatic, endocrine, or nutritional disorders. Its severity ranges from mild, barely noticeable swelling to massive anasarca, frequently accompanied by weight gain, dyspnea, and skin changes.
Earache (Otalgia)
Earache (otalgia) is pain in the external, middle, or inner ear caused by infection, obstruction, trauma, or referred pain, often accompanied by hearing loss, discharge, or vertigo. Its onset, character, and associated symptoms help differentiate underlying causes such as otitis externa, otitis media, cerumen impaction, or barotrauma.
Dysuria
Dysuria is painful or difficult urination often accompanied by urinary frequency, urgency, or hesitancy, usually resulting from lower urinary tract irritation or infection. Its timing, associated symptoms, and patient history help identify underlying causes such as cystitis, prostatitis, urinary obstruction, or chemical irritation.
Dysphagia
Dysphagia is a symptom of impaired swallowing caused by structural, neuromuscular, infectious, malignant, or systemic conditions, often classified by the swallowing phase affected.
Recognizing distinguishing features of each cause is essential for timely diagnosis, prevention of aspiration, and appropriate management.

Dysarthria
Dysarthria is a motor speech disorder resulting from neurological injury affecting speech muscles, with diverse etiologies including degenerative diseases, stroke, toxins, and infections. Diagnosis requires detailed neurologic and speech assessment, and management involves treating underlying causes and supportive rehabilitation.

Diaphoresis
Diaphoresis is excessive sweating triggered by physical, emotional, or pathological stress, often indicating underlying conditions like hypoglycemia, infection, or myocardial infarction. It may be localized or generalized and requires urgent evaluation when accompanied by systemic symptoms.

Hypoactive deep tendon reflex
Hypoactive deep tendon reflexes indicate reduced or absent reflex activity due to dysfunction in the reflex arc. They are associated with neuromuscular, metabolic, toxic, and structural disorders and require careful clinical evaluation to determine the underlying cause.
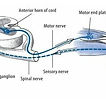
Hyperactive deep tendon reflexes
Are exaggerated reflex responses often caused by upper motor neuron lesions or electrolyte imbalances like hypocalcemia or hypomagnesemia. They may signal serious neurologic, metabolic, or obstetric conditions and require thorough clinical evaluation and appropriate management.











